Plastic extrusion, a method through which plastic shapes profiles are produced, is an important process for many industries. In this process, shapes are produced when molten plastic is forced through a die. Basic plastic extrusion profiles include strips, channels and trim. Read More…
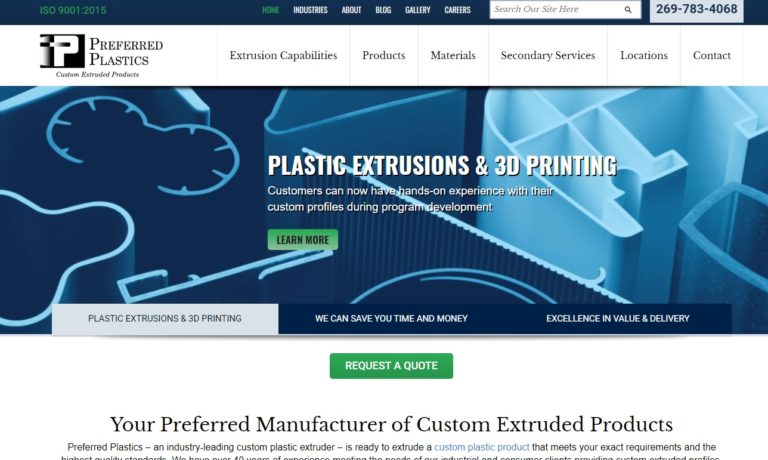
Preferred Plastics is an ISO 9001:2000-certified custom plastic extruder, specializing in rigid, flexible & co-extruded products, including extruded tubing.
Our profile extrusion capabilities are vast and adaptable to meet your specific needs. Whether you require rigid, flexible, dual, or tri-profile extrusions, we have the expertise and technology to deliver. We are dedicated to pushing the boundaries of what's possible in plastic extrusion, and we welcome the opportunity to tackle even the most challenging projects.

We have a long history of providing plastic extrusions. We will proudly serve you and we are committed to quality customer service. Our plastic extrusions are used in industries ranging from automotive to medical.
Crafted Plastics has served the plastics extrusion needs of manufacturers and distributors worldwide since 1982. We craft plastics from a wide array of thermoplastics and are able to extrude basic to complex profiles. Whether you need products made from polyethylene, polycarbonate, polypropylene, PVC or acrylic, we’re your source for extruded plastic profiles or tubing. Call us soon; we look...

Pexco has been a leader in custom plastic extrusion and injection molding, delivering innovative solutions for diverse markets and applications. We have six in-house tool and die centers and expertise in processing over 500 different resins and blends. We specialize in high-performance fluoropolymers, thermoplastics, and elastomers, delivering reliable performance in the most demanding...

At Northland Plastics, we are the experts in unique custom plastic extrusions. We specialize in single and dual durometer profile extrusions, vacuum calibration, automated inline fabrication, custom fabrication, and more. Custom colors and various additives are also available. As an ISO 9001:2015 company, we value product quality, timely delivery, competitive pricing, and excellent customer...

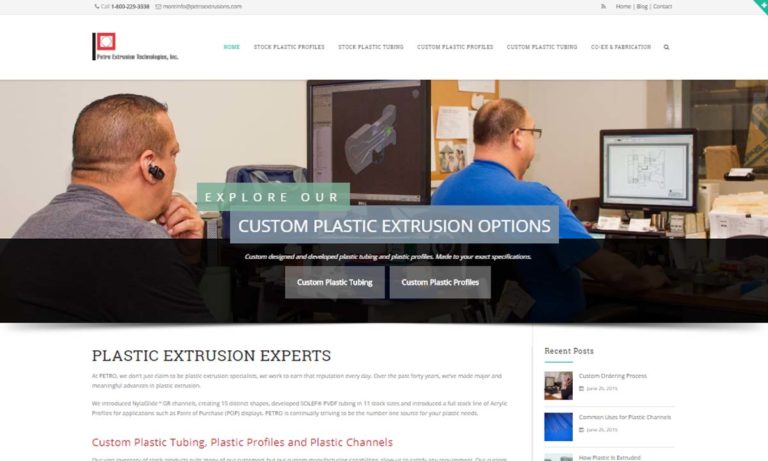
Petro specializes in plastic extrusions, offering our customers many capabilities, such as customized shapes & extruded tubing, along with tape application, coiling & angle cutting.
We develop the most affordable and long lasting plastic extrusions. These extruded materials come in a variety of options and are Polytec Q-1 certified. We offer fast delivery and our customer service team is willing to design a perfect solution for your industry.
A plastic extrusion manufacturer of extruded plastic products, GSH Industries manufactures custom plastic extrusion profiles. We have continually expanded & attained our position as a preferred supplier of quality products & engineering ingenuity.
More Extruded Plastics Manufacturers
Extruded plastics are engineered products created using a process similar in technique to metal extrusion but tailored to harness the unique properties of polymers. Unlike metal extrusion, plastic extrusion is ideal for high-volume, continuous manufacturing, offering exceptional efficiency and versatility due to the lower melting points and malleability of plastics. This process is a cornerstone of modern plastics manufacturing, enabling cost-effective and scalable production for a vast range of industries.
Applications of Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion technology underpins a wide variety of industrial and commercial applications. Its adaptability allows manufacturers to produce parts and products that serve critical roles in:
- Automotive: Door trims, bumper guards, weather seals, dashboards, cable management ducts, and fuel line tubing.
- Food and Beverage: Food-grade tubing, conveyor belts, and packaging films that comply with FDA regulations for food safety.
- Chemical Processing: Corrosion-resistant piping, liners, and containment systems that withstand harsh industrial chemicals.
- Plumbing and HVAC: Pipes, fittings, insulation sleeves, and ductwork components for efficient water and air flow.
- Electronics: Wire insulation, cable jacketing, circuit board spacers, and protective housings for sensitive components.
- Construction and Infrastructure: Window and door frames, wall panels, fencing, siding, and decking materials.
- Water Treatment: Custom extruded filter housings, manifolds, and tubing for municipal and industrial water systems.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: Biocompatible medical tubing, catheters, IV lines, and diagnostic device housings.
Because of its precision and repeatability, plastic extrusion is also employed for producing consumer goods, agricultural products, sports equipment, and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional materials.
Looking for a specific application or industry solution? Try searching for: “custom plastic extrusion for [your application]” or “FDA compliant extruded plastics suppliers”.
Products Produced by Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion manufacturers create an extensive portfolio of products, leveraging the process’s ability to form continuous shapes. Some of the most common extruded plastic products include:
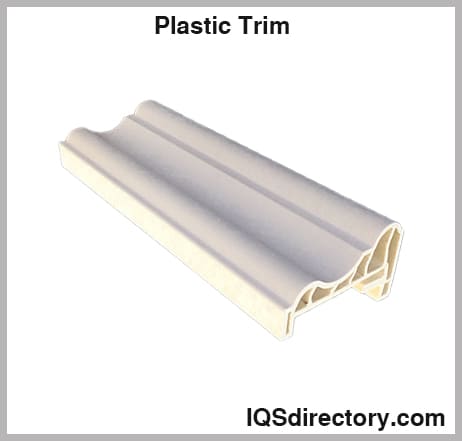
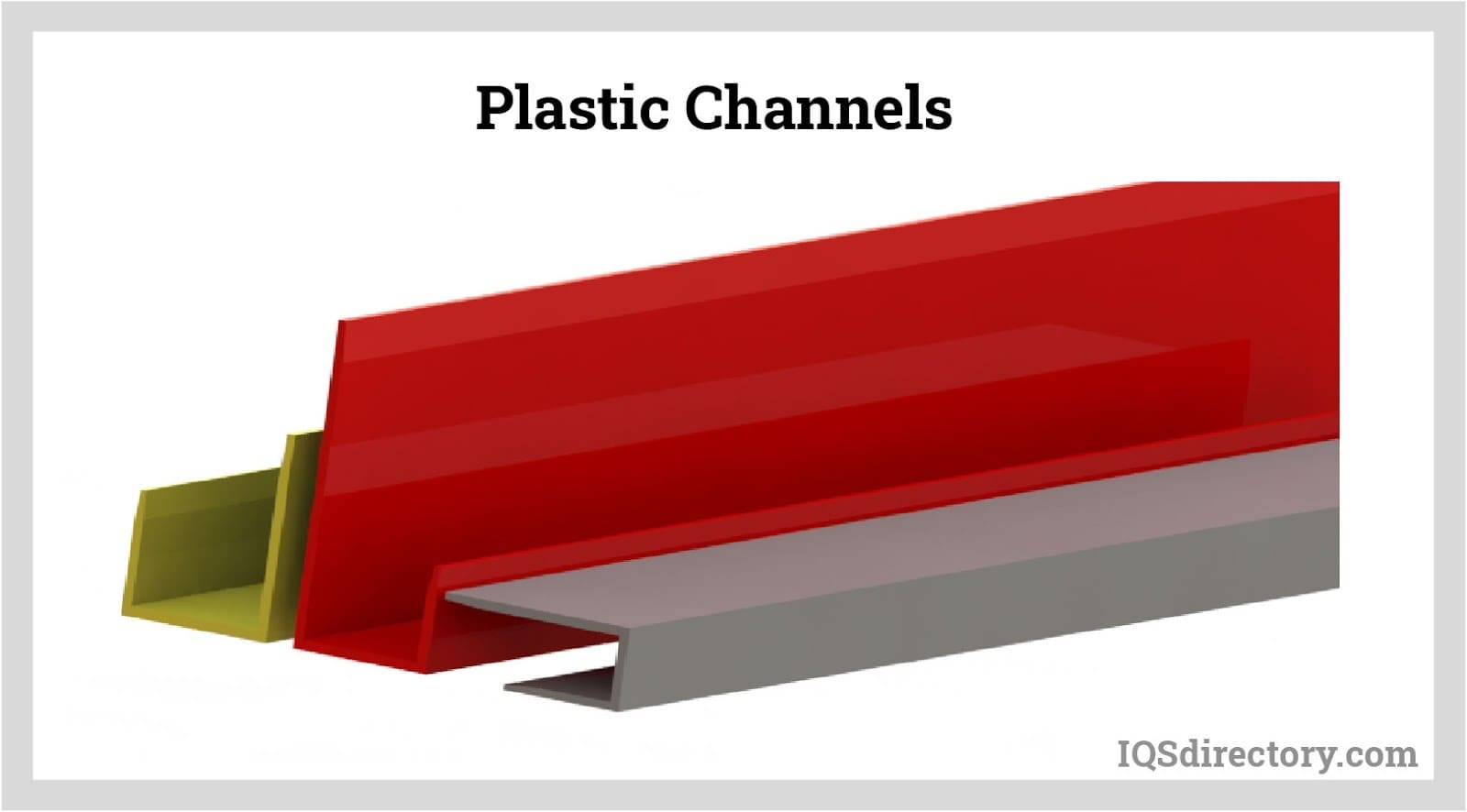
- Profiles – Custom-designed cross-sectional shapes used for window sashes, door seals, display trims, and architectural moldings.
- PVC Channels – Durable and corrosion-resistant channels for wire management, drainage, and framing applications.
- Plastic strips – Flat, flexible, or rigid strips for use in gaskets, spacers, tags, and packaging solutions.
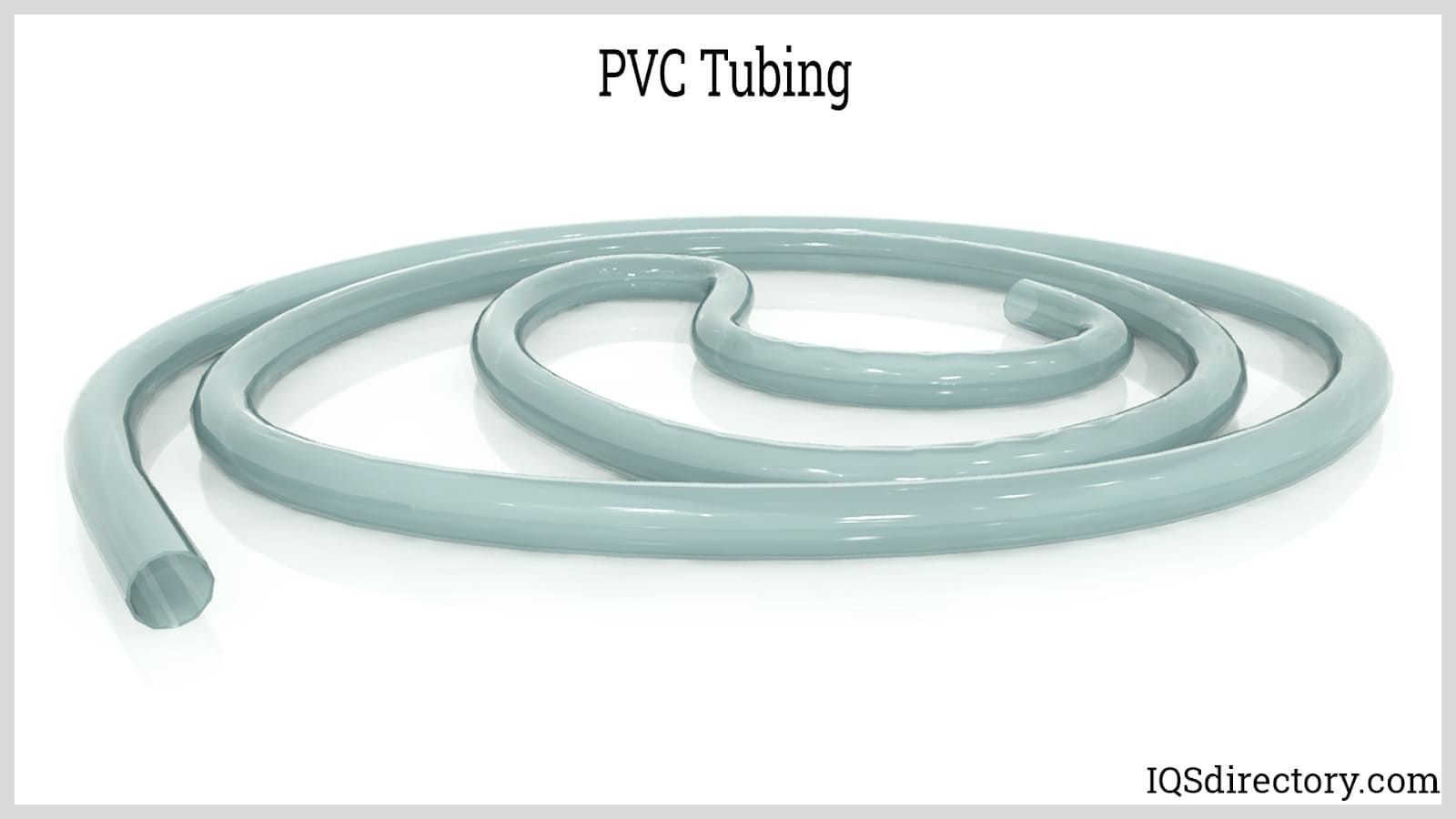
- Tubing – Flexible or rigid tubes for fluid conveyance, insulation, and protective sheathing.
- Engine and Mechanical Parts – Lightweight, heat-resistant components for automotive engines and industrial machinery.
- Decorative and Functional Trims – Automotive exterior trim, appliance edges, and commercial displays.
- Electronic Casings and Enclosures – Molded protective shells for handheld devices, sensors, and control panels.
- Fencing and Deck Railings – UV-stable, weather-resistant extruded products for outdoor environments.
- Window Frames and Door Jambs – Energy-efficient, low-maintenance framing solutions.
- Wire Insulation and Jacketing – Essential for electrical safety and performance.
- Plastic Films and Sheets – Packaging, surface protection, and barrier layers for manufacturing and retail industries.
- Thermoplastic Coatings – Protective layers for corrosion resistance and enhanced durability.
The flexibility of extrusion tooling allows for custom shapes, sizes, and finishes, meeting specific requirements across countless applications.
History and Evolution of Plastic Extrusion
The plastic extrusion process is the result of more than two centuries of innovation in polymer science and manufacturing. The roots of extrusion technology date back to the early 19th century, marked by critical inventions:
- 1820: Thomas Hancock invents the rubber masticator, paving the way for repurposing elastomeric materials.
- 1836: Edwin Chaffee, collaborating with Charles Goodyear, develops the two-roll mixing machine—an essential step toward continuous material processing.
- 1862: Alexander Parkes introduces the world’s first man-made plastic (Parkesine) at the London World Fair, though it was not commercially viable.
- 1870: John Wesley Hyatt patents Celluloid, the first widely used synthetic plastic, opening the door to further innovations like PVC and Bakelite.
As plastic materials proliferated throughout the late 19th and early 20th centuries, manufacturers sought efficient, scalable production methods. The true breakthrough in extrusion came in 1935 when German innovator Ashley Gershoff perfected the thermoplastic extrusion process, soon followed by Roberto Colombo’s introduction of the twin-screw extruder in Italy. These advances set the foundation for today’s high-speed, precision-controlled extrusion lines.
Modern plastic extrusion has evolved to prioritize sustainability, energy efficiency, and precision. Advances include automated process monitoring, recyclable resins, and closed-loop systems to reduce waste. Today, plastic extrusion shapes everything from food packaging to intricate industrial components, and continues to adapt to the demands of new markets and eco-friendly materials.
Materials Used in Plastic Extrusion
Material selection is central to the success of any extrusion project. Each polymer brings unique properties, and engineers often tailor blends to achieve specific performance characteristics. Common plastics used in extrusion services include:
- Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) – Renowned for its flexibility, chemical resistance, and toughness. LDPE is a popular choice for squeeze bottles, bags, tubing, and film applications. Its inertness makes it suitable for food packaging and medical products.
- High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) – Offers greater strength, rigidity, and chemical resistance compared to LDPE. HDPE is widely used in piping systems, geomembranes, industrial containers, and outdoor furniture due to its superior durability and weather resistance.
- Vinyl (Polyvinyl Chloride or PVC) – Available in flexible and rigid forms, PVC excels in insulation, corrosion resistance, and flame retardance. It’s the preferred material for siding, piping, window frames, cable insulation, and flooring, offering versatility for both construction and industrial needs.
- Polypropylene (PP) – Noted for heat resistance, low density, and chemical inertness. Polypropylene is favored for automotive parts, medical devices, reusable containers, and laboratory equipment.
- Polystyrene (PS) – An affordable, easily extrudable plastic used for packaging, disposable cutlery, foam insulation, and consumer products. Its light weight and insulating qualities support diverse applications in the packaging and construction sectors.
- Butyrate – A cellulose-derived polymer prized for its toughness, impact resistance, and dimensional stability. Butyrate is transparent and easy to extrude, making it ideal for visual display components, tubing, and signage.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-Modified) – Combines excellent impact resistance, transparency, and chemical barrier properties. PETG is used for point-of-purchase displays, medical device housings, protective covers, and packaging that requires clarity and toughness.
Other specialty polymers and engineering plastics—such as ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon—are also extruded for high-performance applications. For more complex needs, coextrusion allows multiple materials to be combined into a single product, creating multilayer structures with distinct properties (e.g., moisture barriers paired with impact-resistant layers).
How to Choose the Right Material for Plastic Extrusion?
- Consider chemical resistance needed for the application.
- Evaluate temperature requirements and thermal stability.
- Assess mechanical properties: strength, flexibility, hardness, and impact resistance.
- Factor in clarity and aesthetics, especially for consumer-facing products.
- Ensure compliance with industry standards (e.g., FDA, NSF, RoHS).
- Budget for cost-effectiveness and recyclability.
Need help choosing a polymer? Search: “best plastic resin for [application] extrusion”.
Plastic Extrusion Process Details
The plastic extrusion process is a continuous manufacturing method that can be tailored to the unique requirements of each application. Here’s a step-by-step overview:
- Raw Material Feeding: Plastic granules or resin pellets—often pre-mixed with additives for color, UV resistance, or flame retardance—are loaded into a hopper above the extrusion barrel.
- Gravity Transfer: The granules descend into the barrel, propelled by gravity to ensure consistent material flow.
- Melting and Homogenization: A rotating screw conveys the resin forward through heated zones. The combination of external heaters and frictional heat generated by the screw melts the plastic uniformly, ensuring optimal viscosity and consistency.
- Filtration and Pressurization: The molten plastic is forced through a breaker plate and screen pack, filtering out contaminants, building back pressure, and aligning polymer chains for strength.
- Shaping via Die: The pressurized, molten polymer is extruded through a custom die, forming the desired cross-sectional profile—be it tubing, sheet, channel, or other custom shapes. Virtually any continuous profile is achievable with the right die design.
- Cooling and Solidification: The extruded product must be cooled rapidly and evenly to retain its shape and physical properties. Most commonly, this is accomplished via a water bath or spray, but air cooling or chilled rollers may also be used for precise control. Vacuum calibration may be applied to ensure tight dimensional tolerances.
- Cutting and Finishing: After solidification, products are cut to length or wound onto spools. Secondary processes may include surface treatment, printing, labeling, punching, drilling, painting, or anti-static coatings.
What are the Key Parameters in Plastic Extrusion?
- Extruder temperature profile: Must be carefully matched to the plastic resin for optimal melt flow and product strength.
- Screw design and speed: Dictate throughput, material mixing, and product quality.
- Die design: Determines the final shape, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish.
- Cooling rate: Rapid, uniform cooling prevents warping and stress.
Need troubleshooting tips? Search: “how to prevent warping in plastic extrusion” or “best screw design for PVC extrusion”.
Design Considerations for Plastic Extrusion
Effective plastic extrusion design balances manufacturing efficiency, performance, and cost. Key design factors include:
- Material selection: As detailed above, each plastic offers unique benefits and must be matched to application requirements.
- Die geometry: The die must be engineered for the desired cross-section, tolerances, and wall thickness. Complex profiles may require advanced die design and simulation.
- Process parameters: Temperature, pressure, cooling rate, and screw speed are optimized for each resin and product geometry.
- Production volume: High-volume projects benefit from custom automation and rapid changeover capabilities.
- Color and surface finish: Pigments, additives, and post-extrusion treatments allow for virtually unlimited customization.
- Secondary operations compatibility: Consider downstream processes like cutting, drilling, printing, and assembly.
Manufacturers offer custom extrusion services, tailoring products to meet specific dimensional, mechanical, and aesthetic requirements. If you require a unique profile, collaborate with an experienced extrusion partner to ensure your design is manufacturable and cost-effective.
Machinery and Equipment in Plastic Extrusion
The plastic extrusion process relies on specialized machinery to ensure quality, consistency, and production speed:
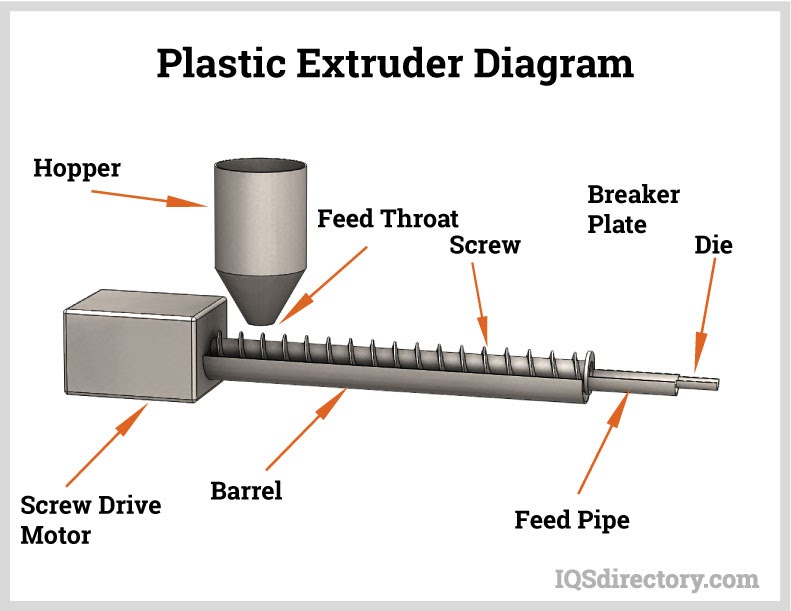
- Extruder Machine: The heart of the process, featuring a feed hopper, heated barrel, rotating screw, and drive motor. Single-screw extruders are common for standard profiles, while twin-screw extruders offer superior mixing, throughput, and flexibility for complex or filled materials.
- Extrusion Dies: Precision-machined metal plates or assemblies that impart the finished shape to the molten polymer. Flat dies are used for sheets, annular dies for tubing, and custom dies for intricate profiles.
- Temperature Regulation Systems: Essential for maintaining precise temperature throughout the barrel, die, and cooling sections. Includes electric heaters, thermocouples, water cooling baths, and air-blast coolers.
- Pullers and Cutters: Ensure uniform extrusion speed and accurate product length.
- Quality Control and Monitoring Systems: Modern extrusion lines feature sensors and automated controls for real-time monitoring of temperature, pressure, dimensions, and surface quality.
Looking for advanced machinery? Search: “high-speed plastic extrusion lines” or “twin-screw extruder for custom profiles”.
Common Machinery Terms Explained
- Hopper: The vessel that feeds raw plastic pellets into the extruder barrel.
- Screw: The rotating shaft that melts, mixes, and pushes the polymer toward the die.
- Die: The shaping tool that determines the product’s final cross-section.
- Calibrator: Device that ensures the extrudate maintains precise dimensions as it cools.
Variations and Related Plastic Forming Processes
Cold Extrusion
Cold extrusion operates below the recrystallization temperature of the material, often at ambient temperature. While more common in metal forming, cold extrusion of certain plastics and rubbers is possible, offering advantages like improved dimensional stability, tighter tolerances, and reduced energy consumption.
Coextrusion
Coextrusion utilizes multiple extruders in a single production line to combine different materials into multi-layered products. This allows manufacturers to produce components with unique surface properties, such as a tough outer shell and a flexible inner core. Coextrusion is common in packaging films, medical tubing, and window profiles where combined functionality is required.
Blow Film Extrusion
Blow film extrusion is a specialized technique for creating thin, flexible plastic films, such as those used for shopping bags and food wrap. The process involves extruding a tube of molten plastic, inflating it with air to form a bubble, and then cooling and flattening the film. This method enables high-speed production of films with uniform thickness and excellent clarity.
Plastic Injection Molding
While similar to extrusion, plastic injection molding is distinct in that molten plastic is injected into a closed mold cavity, forming discrete parts rather than continuous profiles. Injection molding is ideal for producing high-precision, complex components at high volumes, such as bottle caps, automotive parts, and electrical enclosures. Extrusion is better suited for long, continuous shapes.
Benefits of Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion offers a range of unique advantages that make it the preferred manufacturing method for many applications:
- Design Flexibility: Capable of producing complex, custom profiles with tight tolerances.
- Cost-Effectiveness: High-speed, continuous production drives down per-unit costs, especially for large volumes.
- Material Efficiency: Minimal material waste—scrap can often be reprocessed, supporting sustainability goals.
- Versatility: Supports a vast array of polymers, colors, finishes, and additives.
- Scalability: Easily adapted for both short-run prototyping and high-volume production.
- Post-Extrusion Modifications: Products can be cut, drilled, printed, or otherwise modified immediately after extrusion.
- Eco-Friendly Manufacturing: Recyclable resins, low energy consumption, and closed-loop systems support green initiatives.
Want to compare extrusion to other plastic forming processes? Search: “plastic extrusion vs injection molding advantages”.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Plastic Extrusion Manufacturer
Selecting the right extrusion partner is critical to project success. When researching plastic extrusion companies, evaluate them based on:
- Technical expertise in your material, industry, and product type.
- Quality control systems and certifications (ISO, FDA, NSF, etc.).
- Production capacity and lead time to meet your schedule.
- Custom design and engineering support for unique profiles or challenging applications.
- Sustainability initiatives and recyclable material options.
- Customer service and communication throughout the development process.
- Competitive pricing and transparency in quotes.
We’ve compiled a directory of leading extruded plastics manufacturers to help you compare capabilities and request quotes. Explore their company profiles to find a partner tailored to your needs—whether you require rapid prototyping, high-volume production, or custom coextrusion expertise.
Decision-Making Prompt:
Still evaluating suppliers? Ask yourself: “Does this manufacturer have experience with my application and material?” and “Can they scale production if demand increases?”
Frequently Asked Questions About Plastic Extrusion
- What’s the difference between single-screw and twin-screw extruders? Single-screw extruders are simple and cost-effective for standard materials, while twin-screw extruders offer better mixing, throughput, and flexibility for complex, filled, or recycled polymers.
- Can I use recycled plastics in extrusion? Yes! Many manufacturers offer extrusion services with recycled or reprocessed resins, supporting circular economy and sustainability initiatives.
- How do I ensure my product meets regulatory standards? Work with a manufacturer that provides documentation for FDA, NSF, RoHS, or other relevant certifications. Specify compliance requirements during the design phase.
- What are typical lead times for custom extruded products? Lead times vary based on tooling complexity and production volume, but many suppliers offer rapid prototyping and accelerated delivery for urgent projects.
Next Steps: How to Get Started with Plastic Extrusion
Ready to launch your project or need expert guidance? Here’s how to proceed:
- Define your application requirements (material, size, shape, volume, regulatory needs).
- Search for reputable plastic extrusion manufacturers with proven expertise in your industry.
- Request samples and review quality certifications.
- Collaborate on design optimization for manufacturability and cost savings.
- Schedule production and arrange for logistics or downstream processing as needed.
For additional resources and information on plastic tubing and related products, check out our Plastic Tubing website.
Still have questions? Try searching: “plastic extrusion design best practices,” “custom plastic profiles for industrial use,” or “how to choose an extruded plastics supplier.”
With the right knowledge and manufacturing partner, plastic extrusion can unlock innovative, cost-effective, and sustainable solutions for virtually any application.






 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics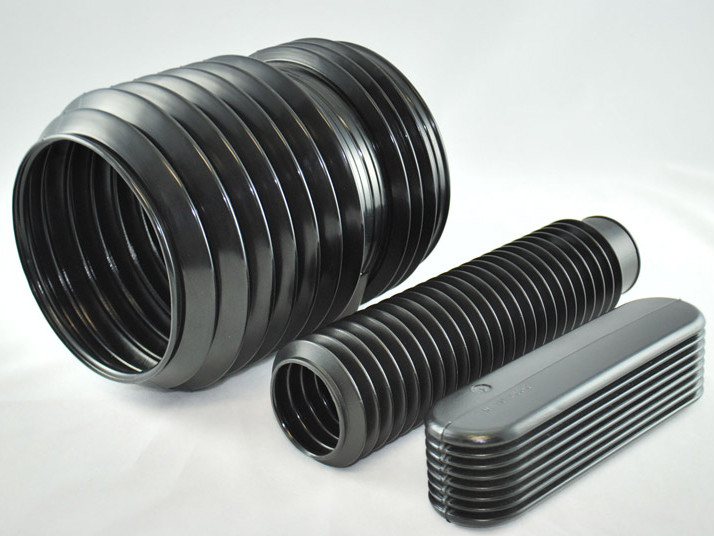 Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding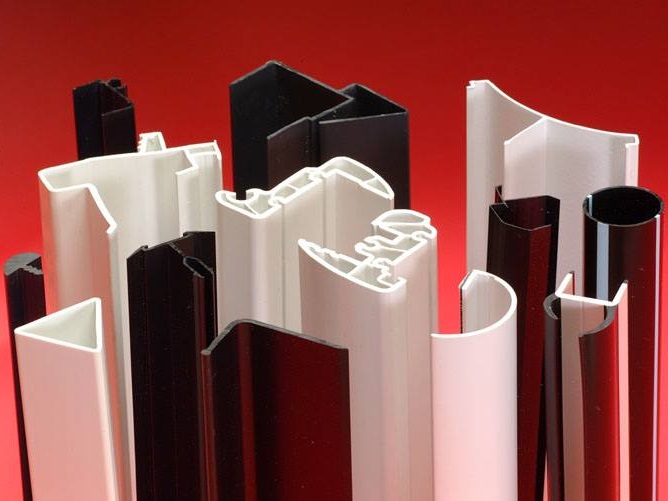 Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services